Ginger is a herbaceous medicinal plant, which is used in cooking as a spice. This is one of the most profitable for planting herbs because of the great demand for it. But at the same time, it is one of the most difficult crops to grow. About how to grow this plant at home in the country in the suburbs, read on in the article.
Is it possible to grow ginger in the suburbs?
Ginger (Zīngiber officināle) grows in India, China, Nepal, Indonesia, Thailand, Japan, Jamaica, Nigeria and other southern countries. And this immediately indicates what environmental conditions are more familiar to him: the climate is tropical and subtropical, frost resistance zones from 9 to 12.
European countries usually import it in large quantities. And despite the inconsistency of climatic conditions that the plant needs for successful growth, they try to grow the plant not only in the tropics, but also in other, cooler climatic zones.

Although the plant itself does not require special care, it will not grow under any conditions. There are several factors that significantly affect the growth of ginger root: climatic conditions and soil conditions. The plant can be planted in any dry place in the home garden, where sunlight illuminates the area for at least 4 hours a day and it rains moderately. It does not respond very well to direct sunlight. Therefore, it is convenient if the area is periodically shaded.
Planting a number of vegetable crops, such as beans, will provide spotty sunlight. In addition, ginger needs to be watered. Using a layer of mulch will prevent direct sunlight, raise the temperature of the soil to a more acceptable root development and keep soil moisture from evaporation.
Did you know? Ginger root will bloom no earlier than 2 years after planting. If you want to plant it in order to get a beautiful ornamental plant, then buy planting material in the nursery, and not in the vegetable store.
The roots will develop well in loose soil rich in organic matter and moisture. But if it rains for a long time or the air temperature drops below + 15 ° C, then the roots will stop developing. Therefore, for the Moscow region, we can recommend the greenhouse method of growing plants. The use of mini-greenhouses, which can be installed directly above the bed in the open ground when weather conditions worsen, is also acceptable.

Suitable varieties for open ground
If you do not plan to grow ginger for a commercial purpose, then there is no point in buying expensive seed rhizomes. Start with any root purchased at the supermarket. It is better to buy it at a point of sale selling organic products. In such stores, the roots are not treated with chemical solutions to slow down or stop growth. So you will be sure that ginger will certainly grow.
The main types of ginger roots:
- green ginger (Baby ginger) - is most often used in cooking because of juiciness and delicate taste;
- hawaiian ginger (Blue hawaiian ginger) - a bluish-colored root with beige pulp, characterized by a sharp taste;
- african ginger (White ginger) Is a tall grass that is grown because of beautiful white flowers. Perfect for indoor plant growing and decorating gazebos;
- yellow ginger (Yellow ginger) - the most common, used for medicinal purposes. It is an excellent analgesic that also has anti-inflammatory effects and is used for wound healing.

Step-by-step instructions for growing
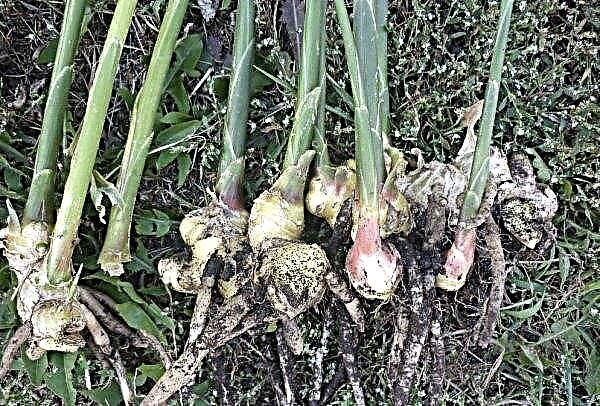
Ginger propagates by seeds or rhizomes. Until use, planting material must be stored in a place protected from pests and diseases. Fresh ginger rhizome in its physiology is very similar to potatoes. Excavated, it has a thin skin and for long-term storage it is necessary that it be roughened.

For this, the rhizome is laid out in direct sunlight for 3–7 days. Ready for planting ginger will have a yellow-brown skin, about 0.5-1 mm thick. Sprouts are formed from the eyes (kidneys) on it. Plant it whole and you will get as many young stalks as many eyes are available.
Cut the rhizome into parts 2-3 weeks before planting, leaving a few eyes in each - and you will grow several separate plants. The weight of each part should be at least 4-6 g. Consider that the larger the piece, the more nutrients it has for development and the more powerful the plant will be. Pieces of the root must be laid down so that the surfaces of the slices are roughened.
Important! It is forbidden to treat the rhizome with any chemicals.
Prepare a container with the nutrient mixture and plant parts of the rhizome in it. Be patient. Sprouts will appear in 5-10 days. All this time the earth needs to be moistened. Do not place the container in direct sunlight to avoid overheating of the soil. After the seedlings sprout, they can be transplanted into the open ground.

Seat selection
You will need a sunny spot with spotty light. The sun should light it 2-5 hours a day. If ginger grows next to other plants, for example, legumes, they will create an excellent barrier for it from sunlight.
Soil preparation
Be sure to remove all weeds during soil preparation. On clay soils, it is recommended to make raised beds. Height - 15 cm, width - 1 m. The distance between adjacent rows - 20 cm. Soil acidity - 5.5–6.5 pH. Landing time is early spring.

Landing
Given the climate of the Moscow region, it may be worth growing plants not in the ground, but in pots. Potted soil when planting is combined with sphagnum moss, compost or other organic matter. For the winter, such plants can be brought into the room to protect them from severe frosts. It is highly likely that the ginger left in the open ground will simply rot during the winter.
Did you know? If you are planting a purchased root, then some gardeners recommend soaking it in warm water overnight. The idea is not bad, because it could be treated with growth inhibitors, and water activates the development of sleeping kidneys.
The root does not need much space. First, it will grow in the form of a compact clot of leaves. The site is dug up for him. If the soil is clay, then it is diluted with organic fertilizers, for example, rotted manure. It will need about 2 buckets per 1 m² of land. Then they make a hole, water it with water and plant a seedling there.
After 2-3 days, when the soil settles, the area around the sprout is mulched. Chips, straw or pine needles are suitable for this. The thickness of the layer is 2-3 cm. It will prevent the growth of weeds, maintain soil temperature and cover the roots from hot sunlight, preventing the moisture from drying out quickly.

Watering and further care
No matter how the root is planted, it needs a lot of moisture for active growth. The soil should never dry. But don't get carried away. If you pour water abundantly, the nutrients will be washed out of it into the lower layers of the soil, from where the root will not be able to get them.
Ginger is a slow-growing plant, and weeds are easily killed if not removed regularly. Blur grass after each watering. Rhizome does not need additional nutrition if you have applied organic fertilizers when planting. In this case, just bring in the following portion of organics every spring and this is enough for excellent growth.
Important! The constant cultivation of ginger in the same area can lead to lower yields. After 2-3 years of continuous farming, a one-year break is required.
If there is heat and the air is too dry, then regular spraying of water or installing nearby water tanks will help moisturize it. Also keep in mind that dryness causes infection with spider mites. Nematodes, slugs, snails, ticks are the main insects that harm ginger. If the plant will grow more than one year, then you will probably come across them.

To combat root pests, the beds are well digged and treated with boiling water before planting. If insects are already detected during growth, the soil is treated with insecticides. From slugs and snails, a bed around is sprinkled with crushed shell rock or coarse sand, which become an insurmountable barrier for them.
Spraying with an insecticidal soap solution helps against ticks and other leaf-eating pests: aphids, thrips. By the end of summer, when the air cools, ginger will begin to die. Reduce watering and let the land dry. This causes the plant to form rhizomes. As soon as all the leaves have wilted, the root is ready for harvest.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting ginger for vegetable purposes begins in 4-6 months. Dig it out carefully so as not to damage the roots. Growing up to the moment of harvesting a full crop takes about 8 months. The time for harvesting comes when the leaves are dry. After digging the plant, break the rhizomes.

Leave a few large ones for planting. They can be transplanted immediately, and the rest can be used in the kitchen for cooking. Also, the root can be peeled, cut into small pieces and frozen. Some housewives make of it alcohol tincture, used for medicinal purposes.
As you can see, it is not so difficult to grow ginger in a summer house in the suburbs. You just need to consider the plant's requirements for weather and soil. Otherwise, ginger is not too picky, but it is very good for health. And these are significant reasons for growing it.