These simple structures can often be found in gardens and summer cottages. Greenhouses from arcs with covering material - they will be discussed in the proposed material, about the features of their designs and the procedure for self-assembly.
Why use greenhouses from arcs with covering material
Such structures, depending on their size and designs, are capable of performing a wide range of tasks, namely:
- The cultivation of heat-loving species of crops in regions with a cold climate.
- Adapting seedlings to growing conditions in the open.
- The cultivation of certain crops (for example, radish) at a time when the soil in the open air is still or is not already sufficiently warmed up.
- Stimulating seed germination.
- Protection of beds from harmful insects.
- Planting protection from animals and birds.

- Such greenhouses have several advantages:
- Light weight and mobility - if necessary, it is easy to move them from one place to another.
- No need to build a foundation.
- Conveniently stored unassembled, do not take up much space.
- Relative cheapness.
- At the same time, certain disadvantages of these structures cannot be discounted:
- The fragility and fragility of the covering material.
- Danger of damage or even destruction of the greenhouse by strong winds.
- The lack of the possibility of additional heating, which, in turn, entails a limitation on the time of planting and harvesting and the range of crops planted in the greenhouse.
Features of greenhouses from arches with covering material
Features of the covered garden are entirely determined by the properties of the material with which the greenhouse is covered. The following are the main types of covering material.
Did you know? Greenhouse — it is the predecessor and simplified seasonal model of the greenhouse.
Polymer film
The most common material made on the basis of polymers is high molecular weight compounds.
- The polymer film is characterized by:
- Cheap.
- Lightness (low specific gravity).
- Easy division into the necessary parts.
- Simple fastening to any frames.
- The inability to break it.
- The ability to obtain the necessary shape, gluing and joining by welding with a soldering iron (iron).
- High light transmission.
- Moisture resistant.
- Frost resistance.
- With sufficient thickness - resistance to precipitation.

- At the same time, the film has certain disadvantages:
- Great heat conductivity.
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- Loss of quality with repeated installation and use.
- Weak resistance to snow load.
Currently, films are produced with additional properties:
- Hydrophilic.
- Antistatic.
- Light stabilized.
- Reinforced.
- Heat resistant.
- Selective.
- Black.
Spanbond
The material is obtained by the method of polymer melting and laying its fibers in an air stream. To protect against the rays of the sun, the melt of stabilizers is included in the fiber.
The main functional use of spunbond:
- Accelerating the warming of the earth and stimulating rapid seedlings.
- Protecting the soil from drying out and, thereby, saving watering.
- Protecting landings from the cold.
Spanbond is different:
- Good breathability.
- Homogeneous structure (provides uniform distribution of heat and humidity and microclimate stability).
- Light transmission.
- High thermal insulation.
- Low specific gravity.
- Good durability, resistance to wear and tear.
- Resistance to atmospheric effects (preservation of properties at a temperature range from + 55 ° С to + 100 ° С).
- Resistant to septic bacteria and mold.
- Inertness to various kinds of chemical compounds (the use of pesticides does not affect the material).
- No toxicity for planting.
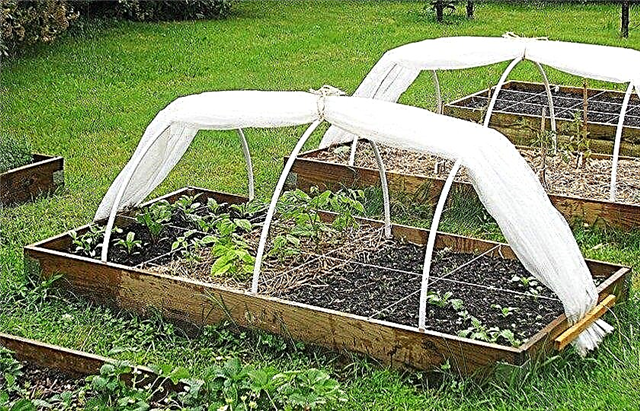

Polycarbonate
This is a plastic made from polymer raw materials. For equipment, greenhouses use sheet honeycomb polycarbonate - a polymer in the form of a multilayer panel with internal stiffening ribs and a special coating from exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- Polycarbonate is characterized by:
- Transparency.
- Durability.
- Flexibility.
- High thermal insulation.
- Ease.
- Easy to mount.
- Resistance to temperature changes.
- Security.
- Chemical resistance.
- Environmental friendliness.

Varieties of designs
There are several design options for such structures, and they depend on the material from which the arcs are made:
- Arch made of dense and hard wire, covered with a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sheath, which protects against rust and mechanical damage.
- An arch made of metal tubes with a diameter of 10-12 mm, which are also protected by a PVC shell. These arcs are characterized by increased rigidity and stability.
- Arch of plastic pipes with a diameter of 20-30 mm. Less design - less reliability and durability, plus the risk of damage from strong winds.
How to make greenhouses from arches with covering material with your own hands
Having considered the structural varieties and types of covering material, you can go to the options for self-installation of these structures.
Preparation for construction: drawings, dimensions
Such a greenhouse will not require a complex drawing scheme with an exact indication of the dimensions that determine the construction of the structure. The size of the plot for the greenhouse will be decisive. Next you only need to determine the height and width of the arcs, as well as their number.
Did you know? Greenhouses first arose in ancient Rome when Roman gardeners in the afternoon rolled out their plants in small carts in the sun, and at night drove into heated rooms.
Calculation of the required amount of materials and tools
When calculating the materials, one must keep in mind which crops will be grown in the building: if the plants are kept only during the initial period of their growth, then an arc will be required up to 75 cm high; if you plan to grow crops to their full maturity or just high crops, then you will need a meter-high arch. Rule: the higher the arc, the more covering material.
The width of the arcs depends on the area under the frame of the structure. Usually, it is from one to one and a half meters.
Taking into account the length of the greenhouse (for example, 6 m), the number of arches is calculated. As a rule, they are installed with an interval from 80 to 100 cm, so for a six-meter greenhouse you will need 7-8 arches.
Covering material is sold in running meters, so you need to buy it with a margin both in length and in width. For a six-meter greenhouse, it will need 8 m, taking into account the closure of the "entrance" and "exit" to the greenhouse.
The width of the covering material must be calculated based on the entire length of the arc. It is measured in place with a simple tape measure.
For the construction, you will also need wooden boards (4 pieces: 2 long and 2 short with a size equal to the base of the structure) and reinforcement (for fastening the top of the arches). If it is not possible to prepare a wooden base, then arches of any structures are simply dug into the ground (to a depth depending on the material of which the arc is made).As for tools, a hammer and a machine (fixture) for bending pipes will be needed.

Step-by-step instruction
First of all, it is necessary to take into account the requirements for the future place where the greenhouse will be built.
These requirements are as follows:
- Sufficient illumination of the site.
- Location on the southern, southwestern or eastern part of the country (garden) plot.
- Good protection from the cold north wind.
- Advance preparedness of the soil - feeding with minerals and organic matter, diligent digging and cleaning of weeds.
Important! The most suitable for the construction of an arched greenhouse with covering material is a site that is protected by a fence or what-either constructions.
Installation of a greenhouse from metal-plastic arches
Construction procedure:
- In the manufacture of a framework of 200–250 cm, plastic pipes are bent and attached with special brackets to the bases of wooden boards fixed in place. As an alternative (for a six-meter greenhouse) - at the same distance from each other with an interval of 80–100 cm, 14 pieces of reinforcement are driven into the ground, onto which bent pipes are then put on.
- To give the structure better strength and stability, its top is “stitched” with reinforcement (PVC pipe or just a board).
- The complete frame is covered over its entire length with prepared covering material, and at the same time it must lie “lapped” with the ground from the ends - to prevent destruction and blowing of the structure by the wind.
- If an inexpensive covering material was used, then on the sides it can be pressed to the ground with any weights (for example, stone, brick), if the material was used more expensive - it is attached to the ground using special brackets.
Video: DIY greenhouse from arcs
Installation of a greenhouse from propylene plastic arches
The construction action algorithm is as follows:
- A propylene hose (or simple thick-walled) is cut into identical fragments of 200–250 cm.
- Cut pieces of hose inside are reinforced with thick wire.
- Then, according to the inner diameter of the hose, stakes are prepared (wooden or iron) in length from half a meter.
- Stakes made in two parallel rows are installed in the ground with a distance (depending on the width of the greenhouse) of one and a half meters and an installation step of 80-100 cm.
- After that, one edge of the reinforced hose is put on one stake, the second edge on the parallel. And so on to the edge.
- For stable attachment of the hose to the stakes at its ends, longitudinal cuts of 10 cm are made. Then these places are pulled together with an iron clamp.
- A reinforced hose is laid over the structure for the bundle, connecting the greenhouse as a whole. The hose is screwed to the arches with wire.
- The assembled and fastened structure is completely covered with covering material, which is fixed on the sides with special fastenings to the base, or if it is absent, it is pressed to the ground by heavy loads. In regions with frequent strong winds, the ends of the constructed greenhouse made of metal-plastic arches are strengthened by props made of timber.
Metal profile mounting
To erect such a structure, a pipe bender or apparatus for welding will be needed.
Installation Order:
- With a pipe bender or a welding machine, seven pipes of the same length (200–250 cm) are bent to the desired circumference.
- With two parallel lines at the same distance from each other with a pitch of 80–100 cm, 14 half-meter pieces of reinforcement are driven into the ground.
- Prepared arched pipes are put on the stakes remaining on the surface and fixed on a wooden base pre-prepared and laid along the length of the greenhouse.
- Using a long reinforcement or a thin pipe, a “bandage” or greenhouse screed is made on top. Connection with arches can be a collar or welding.
- The finished structure is completely covered with material that is fixed on the sides of the base (for example, a furniture stapler).
Important! So that the covering material is not torn off the frame by the wind, it is fastened with plastic clips sold in a specialized retail network.
Overview of arched greenhouses for industrial production
In cases where there is no opportunity or time to engage in arranging greenhouses with arches and covering material yourself, finished industrial products will come to the rescue.
Greenhouse "Agronomist"
The basis of the mini-greenhouse is durable plastic pipes of 20 mm in diameter. The width of the structure is up to 120 cm, height is up to 80 cm and length is up to 8 m. The covering material is protected from ultraviolet rays and connected to arcs. Pegs and clips are also included.

Greenhouse "Good season"
The height of the structure is 95 cm, width 120 cm, length from 4 to 8 meters. Installation of the frame - on the clamping U-shaped pegs. Arc length of 230 cm - sewn into the material with UV stabilizers.

Greenhouse "Dayas"
The basis of this garden under the roof are polymer arches and sewn-in covering material. Pipes 200 cm long and 20 mm in diameter. Attached to the ground with legs. The set of pipes is designed for the construction of a 4-6 meter tunnel with a height of 70 cm and a covering material width of 210 cm.
Easy to assemble, not requiring special material and time-consuming greenhouses from arches with covering material are a convenient and practical solution to many problems faced by summer residents and gardeners.