The climatic conditions of Siberia do not allow growing vegetables in the open field. To do this, you need a quality greenhouse. One of them is Siberian. About the characteristics of the model, its assembly use, read further in the article.
Features of the climate of Siberia
Siberia does not pamper vegetable growers with a long summer. A climate favorable for vegetables lasts no more than 100 days, and a long winter is accompanied by snow and frost. Often, the snow lingers on the ground until the end of May, and the first frosts can strike in August.
Other climate features:
- freezing soil;
- lack of sunlight;
- strong cold winds.
In this regard, if you decide to grow vegetables in Siberia, you will definitely need a greenhouse. A convenient solution to the issue is sectional construction. They are standard, from them you can create a structure of any length by adding or removing sections.
Did you know? The first greenhouses were created by gardeners of the Roman emperor Tiberius. These were moving wagons covered with pieces of transparent mica. They were created for growing cucumbers, which the emperor loved so much.
Polycarbonate greenhouse design for Siberia
The most common design is arched. This form was also chosen for the "Siberian" greenhouse. The arcuate surface scatters the sun better than others. This provides the plants with optimal light conditions. In winter, the arch is convenient because snow does not accumulate on its surface. In the manufacture of the frame, a galvanized steel pipe with a cross section of 25 × 25 mm, 40 × 20 mm is used. Steel is not subject to corrosion and has a high tensile strength. Zinc plating gives it a presentable appearance. The frame connections are made by T-shaped elements and bolted. You can also apply welding, but then the structure will be one-piece, and you will not be able to move it to another place. Consists of 6 or more sections, depending on size. The greenhouse is available in several sizes: an area of 12, 18, 24 and 30 m².
Steel is not subject to corrosion and has a high tensile strength. Zinc plating gives it a presentable appearance. The frame connections are made by T-shaped elements and bolted. You can also apply welding, but then the structure will be one-piece, and you will not be able to move it to another place. Consists of 6 or more sections, depending on size. The greenhouse is available in several sizes: an area of 12, 18, 24 and 30 m².
Dimensions of these models: 4.2 × 3 × 2.1 m; 6.3 × 3 × 2.1 m; 8.4 × 3 × 2.1 m; 10.5 × 3 × 2.1 m. The coating is made of polycarbonate panels. The material perfectly transmits light, durable, but it easily restores shape after exposure to external factors. Polycarbonate is a new material, the sheets of which withstand temperatures from –30 ° C to + 100 ° C. In addition, it is 50 times stronger than glass and 12 times lighter.
Technical specifications:
- permissible mechanical load: 40 kg / m²;
- resistance to gusts of wind up to 22 m / s;
- good light transmission;
- has low thermal conductivity;
- easy to assemble and dismantle.
Polycarbonate greenhouses have many advantages. They are provided with the qualities of the material - polycarbonate. It is shockproof, resistant to loads, non-combustible, easy to bend, but resists mechanical damage. Deficiencies have not yet been noticed.
Marking the site and creating the foundation
Given that the Siberian soil freezes 2–3 m in depth, installation of the foundation is desirable. This will ensure a comfortable temperature regime for the root system of plants. Choose a site that is well-lit and even, or with a slope to the south. Avoid areas that will be constantly obscured by buildings or tree crowns.
The long side of the structure should be north-south. On the north side, any natural barriers should cover it from the wind. The future site for the foundation needs to be cleaned of weeds, small debris and leveled. Mark the area of the future greenhouse with pegs, tape measure and a building cord.
Did you know? It is not necessary to install a greenhouse under constant sun. For most plants, it is preferable to have bright light in the morning and shade in the afternoon. The shadow also creates coolness and does not allow the air inside to overheat.
Also prepare the tools and materials to create the foundation:
- building materials - sand, concrete, reinforcement;
- construction tools - a container for the preparation of a mortar, a concrete mixer, a trowel, buckets, a drill, a grinder and disks for it, a building level and a tape measure, a shovel.
There are several ways to fix the greenhouse on the ground. The simplest is to drive metal pins into the ground at regular intervals and attach the base of the structure to them. The most difficult thing is to make a foundation, just like for any building. The layout of the greenhouse.
The layout of the greenhouse.
For a conventional foundation:
- Dig a pit to the size of the structure.
- Install the formwork, checking it by level.
- Make a sand and gravel pillow.
- Install reinforcement and pour concrete (1 part of cement is mixed with 3 parts of sand and water is added to obtain a plastic mass).
- After 2 weeks, the formwork is removed and installation of the greenhouse on the prepared base begins.

The greenhouse "Siberian" do it yourself
Assembly instructions for any design are provided. But even without it, all components are simple, and the assembly process is understandable. The frame is assembled with self-tapping screws supplied. When installing polycarbonate, self-tapping screws with a rubberized head are used. This ensures a snug fit and prevents moisture from entering the joint.
Important! It is recommended to install additional fastenings for the roof, as it is more susceptible to rainfall.
Assembly
The sequence of actions during the assembly of the greenhouse (from a pipe 20 × 40 mm):
- Assemble the bottom base.

- Attach to the foundation.
- Install arcs in the lower base.
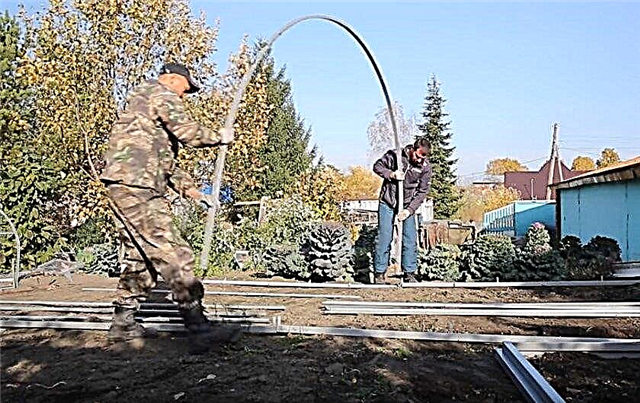

- To connect and fix lateral and top cross-pieces on arches.
- Install the ends.

- Tighten and check all bolted connections.

- Screw the corners on the lower base.

Sheathing
Polycarbonate sheets can be cut with an ordinary sharp knife. Standard sheet thickness is 4 mm. When cutting off "excess" material, use metal elements as auxiliary for the cut line.
Casing Assembly:
- The first polycarbonate sheet is cut in half, according to the size of the ends.

- Remove the protective film from the sheet.

- Fasten the sheet to the end. The marked side of the sheet (the one on which the film was) should be turned towards the sun. The inner is the ribbed part.
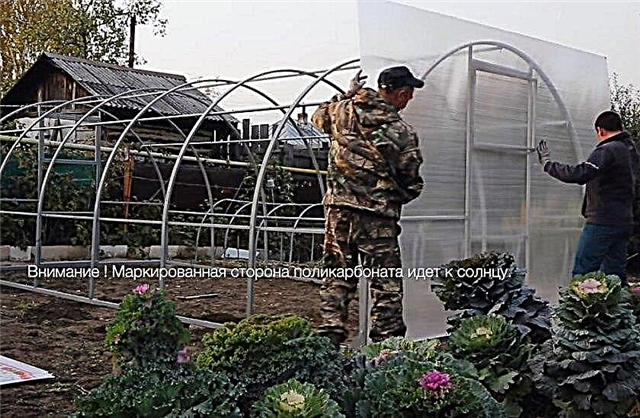

- Hinges are cut in it, as well as a double door. It can open like a window.

- Carefully cut off excess polycarbonate to fit the ends of the greenhouse. It is convenient to lead the knife along the arc when trimming.

- The size of the polycarbonate sheets is able to cover the greenhouse in an arc. To cover the structure, 3 sheets are enough. They are attached to the arches of the greenhouse.

- Joints of sheets can be sealed with sealant.

To improve thermal insulation, you can sheathe the greenhouse with sheets in 2 layers: external and internal. The thickness of the layer between them will be 2 mm, and this will significantly affect the thermal regime inside the structure.
Important! Do not confuse the sides of the sheet, otherwise they will quickly fail under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
Optional equipment
To regulate the microclimate inside the greenhouse, create a ventilation system. This will remove exhaust air and reduce humidity. Manual ventilation is organized by opening the window and door. This is cheap, but will require human intervention. To make the process automatic, use various devices.
A simple and reliable system - ventilation with a hydraulic cylinder. The principle of its action is that there is a working fluid in the tank, which can expand when heated. As it expands, the window opens and vice versa. The smooth opening and closing of the transom affects the microclimate more naturally than the sudden opening of the door. Hydraulic cylinder on the window. In the conditions of short summers and short daylight hours, the greenhouse can also be equipped with additional lighting and heating. Lamps are mounted on the upper crossbar or side racks. The most modern way of lighting is LEDs. Their light spectrum is as close as possible to the sun and smooths the transition between natural and artificial lighting.
Hydraulic cylinder on the window. In the conditions of short summers and short daylight hours, the greenhouse can also be equipped with additional lighting and heating. Lamps are mounted on the upper crossbar or side racks. The most modern way of lighting is LEDs. Their light spectrum is as close as possible to the sun and smooths the transition between natural and artificial lighting.
Tips for maintenance, operation of the greenhouse
If, after harvesting, leave the harvest in the greenhouse until spring, during this time a lot of pests and germs multiply. In the autumn, tops and other plant residues are necessarily removed, the irrigation system is removed or preserved for the winter, and auxiliary equipment is removed. Panels can be washed with ordinary laundry soap both outside and inside. The joints of the frame can be cleaned with a soft brush.
Quickly and reliably disinfect the entire space conveniently with the help of a sulfuric checker. The peculiarity of sulfuric smoke is such that it easily penetrates into the ground and inaccessible places. At the same time, both microbes and pests die. But you need to use a sulfur checker in accordance with the instructions, since the substance is toxic to humans. The greenhouse should be tightly closed, and you can enter there no earlier than 3 days after the end of processing. Some gardeners advise creating a reinforced structure by installing additional elements. These can be duplicate arcs or crossbars. Arched roofs are adapted so as not to accumulate snow. But in winter, after heavy snowfalls, it is advisable to check the integrity of the structure and, if possible, remove snow if it is on the roof or near the walls. It is necessary to remove snow from the walls in order to make way for the one that will fall from the roof.
Some gardeners advise creating a reinforced structure by installing additional elements. These can be duplicate arcs or crossbars. Arched roofs are adapted so as not to accumulate snow. But in winter, after heavy snowfalls, it is advisable to check the integrity of the structure and, if possible, remove snow if it is on the roof or near the walls. It is necessary to remove snow from the walls in order to make way for the one that will fall from the roof.
Did you know? The first modern greenhouses were created by Italians. The need arose during the era of the great geographical discoveries. Exotic plants from the southern countries were beautiful, but needed to create conditions suitable for them.
In the spring, the greenhouse needs to be ventilated, the damaged elements repaired, the cracks treated with sealant, lubricated or the opening mechanisms repaired. Before starting field work, it is advisable to disinfect the soil from phytopathogens with a 3% solution of copper sulfate. There are no difficulties with installing the Siberian greenhouse. With proper care, it will last for many years, providing plants with acceptable conditions for growth and development in an unfavorable climate.